Introduction: FL is the most common indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the Western world. FL may cause disease-related symptoms, and patients with high-risk disease usually require systemic therapy. BR is commonly used as first-line therapy for high-risk FL, and the addition of bortezomib to a BR backbone has been studied (Evens A et al. Clin Can Res 2020). Little is known about how these therapeutic options impact patients' health-related quality of life (HRQL). To fill this gap, patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were administered to patients enrolled on E2408 to quantify symptom burden and effects of BR versus BVR induction on HRQL.
Methods: Patients (n=258) randomized to receive 6 cycles of BR or BVR induction completed PROs assessing neurotoxicity (FACT/GOG-Ntx) at the beginning of each treatment cycle. Additional PROs measuring fatigue (FACT-F), lymphoma-specific concerns (FACT-Lym) and HRQL (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General; FACT-G) were completed at baseline, mid-treatment (MT; cycle 3/4) and end of induction (EOI; cycle 6). Paired t-test was used to assess PRO score changes from baseline to MT and EOI within BR or BVR group. Two-sample t-test was used to compare change scores between groups at MT and EOI, respectively. Univariate analyses with a linear model identified patient baseline characteristics and clinical factors (age, sex, stage, performance status, # extra nodal sites, FLIPI, GELF, bone marrow involvement, elevated LDH, palpable splenomegaly, B-symptoms, CRIS) associated with PRO change scores from baseline to EOI, adjusting for treatment group. A multivariate model was built with backward variable selection approach for each of the PROs.
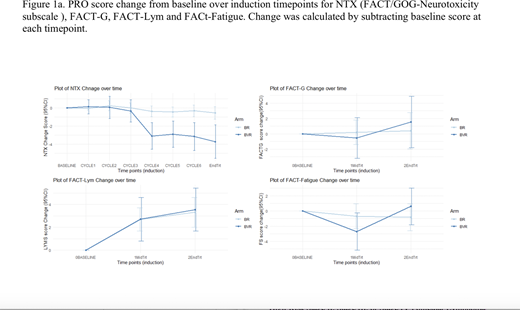
Results: As shown in Figure 1, compared with baseline, patients randomized to BVR reported significantly worse FACT/GOG-Ntx scores at cycle 4, which continued to end of induction (FACT/GOG-Ntx change scores -2.91 to -3.73; p < 0.001). Neurotoxicity remained stable for patients treated with BR (Ntx change scores -0.02 to -0.55). FACT-Fatigue scores indicated worse fatigue at MT compared to baseline for patients receiving BVR (-2.7, p<0.05), yet they remained stable for BR. FACT-Lym scores were significantly higher at MT (BR: 2.69, p<0.001; BVR: 2.71, p=0.007) and end of induction (BR: 3.32, p<0.001; BVR: 3.55, p<0.001) compared to baseline, signifying a reduction in lymphoma-related symptoms in both arms. FACT-G scores were comparable between treatment arms at each time-point and did not change significantly from baseline to end of induction.
Univariate analyses among all patients identified older age and the absence of palpable splenomegaly at baseline as associated with worse FACT-Lym, FACT-Fatigue, and FACT-G change scores, signifying less improvement in lymphoma-related symptoms, fatigue and HRQL from baseline to end of induction (p<0.01). The presence of B-symptoms at baseline was associated with a greater reduction in lymphoma-related symptoms and fatigue from baseline to end of induction (p<0.01). Higher ECOG performance status was only associated with higher FACT-Fatigue change score, suggesting more improvement in fatigue for those with worse performance status at baseline. A multivariate model generated similar results.
Conclusions: Despite worse treatment-related symptoms throughout induction, the addition of bortezomib was associated with comparable overall HRQL to those treated with BR. Both treatments were associated with a reduction in lymphoma-related symptoms from baseline to end of induction, likely contributing to stable HRQL throughout treatment despite treatment-related symptoms. Findings also suggest that a subgroup of patients, particularly those who are older, may experience fewer improvements in lymphoma-related symptoms. This underscores the potential need for closer monitoring and clinical management of these patients. Collectively, results are likely to be encouraging for patients experiencing lymphoma-related symptoms, for whom the symptom burden associated with treatment may be worth the trade-off given the potential for improved disease-related symptom control.
Evens:Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria; MorphoSys: Consultancy, Honoraria; Research To Practice: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Epizyme: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Mylteni: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Advani:Celgene, Forty Seven, Inc., Genentech/Roche, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Kura, Merck, Millenium, Pharmacyclics, Regeneron, Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals, Cell Medica, Celgene, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, KitePharma, Kyowa, Portola Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Takeda: Consultancy. Ansell:Trillium: Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; AI Therapeutics: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding. Winter:Norvartis: Consultancy, Other: DSMB; Ariad/Takeda: Consultancy; CVS/Caremark: Consultancy; Delta Fly Pharma: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Epizyme: Other: DSMB; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: advisory board; Karyopharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: advisory board. Cella:FACIT.org: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: President; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pled Pharma: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Clovis: Research Funding; Alexion: Research Funding; Apellis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Kiniksa: Consultancy; IDDI: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; ASAHI KASEI PHARMA CORP.: Consultancy; Oncoquest: Consultancy; Mei Pharma: Consultancy; Ipsen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Evidera: Consultancy; DSI: Consultancy, Research Funding; BlueNote: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; PROMIS Health Org: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other. Kahl:ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BeiGene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche Laboratories Inc: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics LLC: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy; Acerta: Consultancy, Research Funding. Wagner:Celgene Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Connect Multiple Myeloma Registry: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.